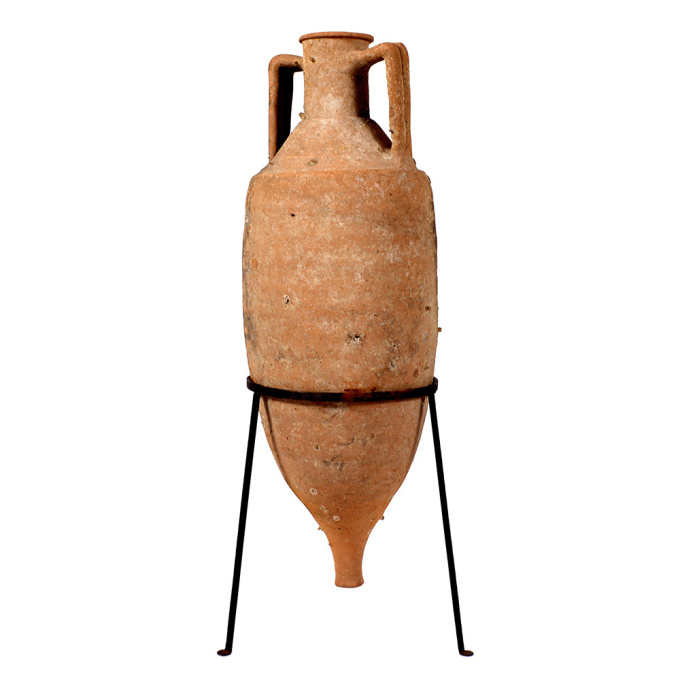
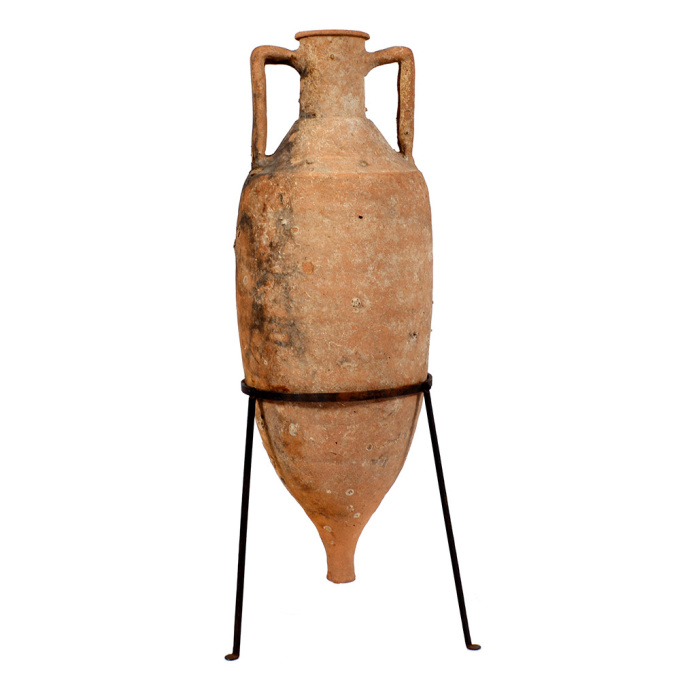
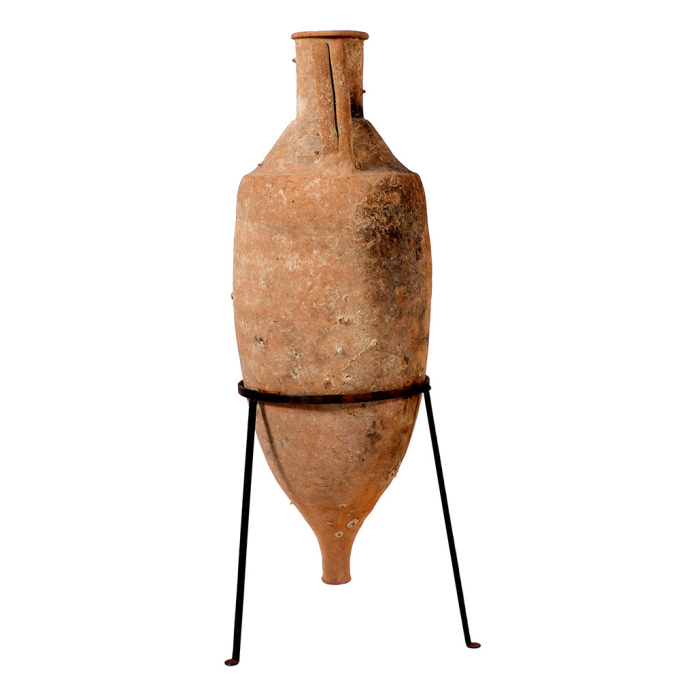
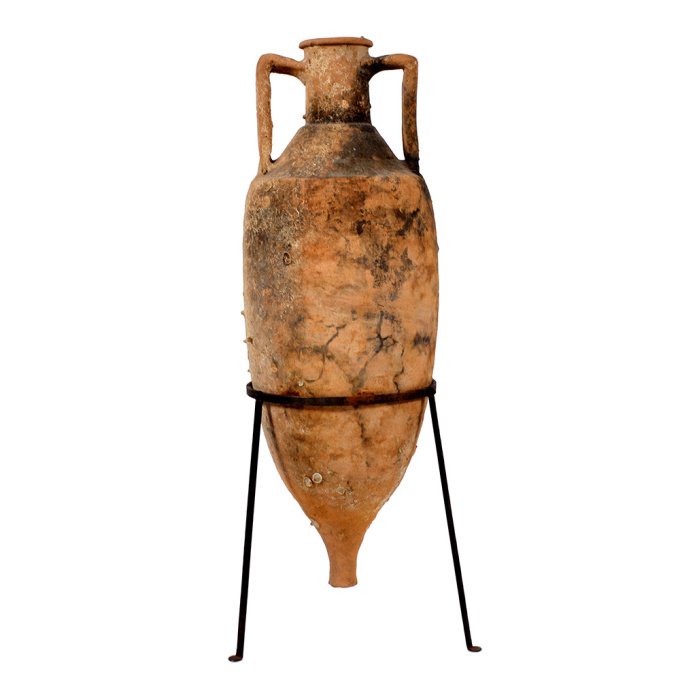
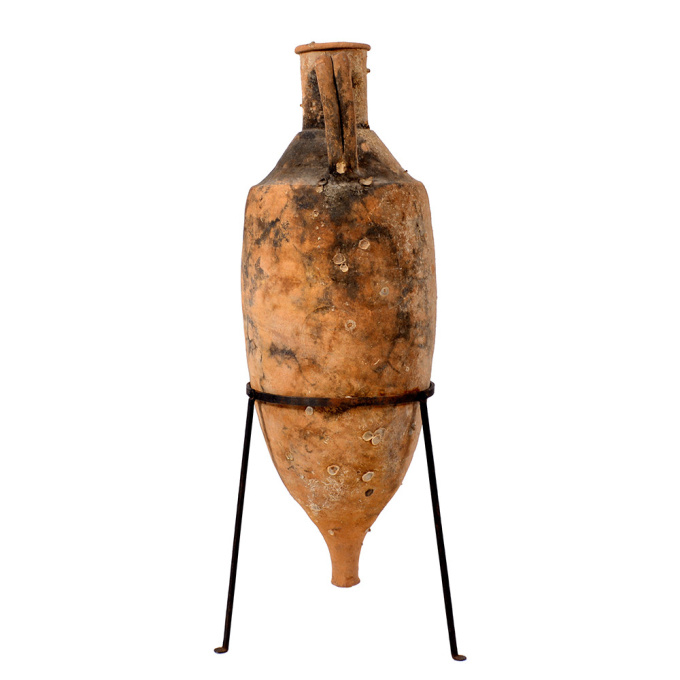
Un ánfora romana de transporte de vino de terracota naufragada 100 BC - 100 AD
Artista Desconocido
TerracotaCerámico
91 cm
Actualmente no disponible a través de Gallerease
- Sobre la obra de arte
This amphora type was based on prototypes from the Aegean island of Cos (Koan type). It has a simple ring-like rim with circular section, and a straight neck ending in a marked shoulder. With a cylindrical body and a solid cylindrical spike. The handles, which comprise two parallel clay shafts with a characteristic bifid section, are flexed and join the amphora immediately below the rim and on the shoulder close to its junction with the neck. With some marine encrustation to one side from long-term underwater exposure, while the other side was most likely submerged in sand and therefore protected. The amphora is fully intact and offered including stand. 91 cm (h) Type: Dressel 2-4 Italian; Koan amphora; Peacock & Williams 10 Ex German private family collection, owned since the 1950s The precise origin of domestic viticulture and winemaking in Rome has not been determined. Early Roman culture was sharply influenced by the ancient Greeks, which makes it likely that the Mycenaean Greeks had some influences in the Roman wine culture through early settlements in southern Italy. Because the ancient Greeks saw wine as a staple of domestic life and a viable economic trade commodity, their settlements were encouraged to plant vineyards for local use and trade. Southern Italy’s abundance of indigenous vines provided an ideal opportunity for wine production Wine had religious, medicinal and social roles that set it apart from other Roman cuisine. Wine, like in Greek culture was mixed with water, and both cultures held banquets, where wine was used to show off wealth and prestige. As Rome entered its golden age of winemaking and the era of expansion, a “democratic” approach to wine started to emerge. Wine was increasingly viewed as a necessity of everyday life rather than simply a luxury enjoyed by the elite. It became available to slaves, peasants and aristocrats, men and women alike. The widespread planting of grapes ensued from the need to serve all classes of society, but was also given impetus by the changing Roman diet. In the 2nd century BC, Romans began to shift from meals consisting of moist porridge and gruel to those more bread-based; wine aided in eating the drier food.
- Sobre el artista
Puede suceder que un artista o creador sea desconocido.
Algunas obras no deben determinarse por quién está hecho o por (un grupo de) artesanos. Algunos ejemplos son estatuas de la Antigüedad, muebles, espejos o firmas que no son claras o legibles, pero también algunas obras no están firmadas en absoluto.
También puedes encontrar la siguiente descripción:
•"Atribuido a …." En su opinión, probablemente una obra del artista, al menos en parte.
•“Estudio de….” o “Taller de” En su opinión, una obra ejecutada en el estudio o taller del artista, posiblemente bajo su supervisión
•“Círculo de…” En su opinión, una obra del período del artista que muestra su influencia, estrechamente asociado con el artista pero no necesariamente su alumno.
•"Estilo de …." o “Seguidor de…”. En su opinión, una obra ejecutada al estilo del artista pero no necesariamente por un alumno; puede ser contemporáneo o casi contemporáneo
•"Manera de …." En su opinión una obra al estilo del artista pero de fecha posterior
•"Después …." En su opinión, una copia (de cualquier fecha) de una obra del artista
•“Firmado…”, “Fechado…” o “Inscrito” En su opinión, la obra ha sido firmada/fechada/inscrita por el artista. La adición de un signo de interrogación indica un elemento de duda.
•“Con firma…”, “Con fecha…”, “Con inscripción…” o “Lleva firma/fecha/inscripción” en su opinión la firma/fecha/inscripción ha sido añadida por alguien que no es el artista
Related artworks
Artista Desconocido
UN NETSUKE MARINE MARFIL DE UN HOLANDÉS CON UN VENTILADOR CHINO18th century
Precio a consultarZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
1 - 4 / 12Artista Desconocido
The bell of the VOC fortress in Jaffna, Sri Lanka1747
Precio a consultarZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
 curada por
curada porDanny Bree
1 - 4 / 13Klaas II Mobach
Hanna Mobach, daughter of the sculptor Klaas Mobach, reading1950 - 1970
Precio a consultarKunsthandel Pygmalion
1 - 4 / 24